Promoting Your Brand
High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is a common condition affecting the body's arteries. It happens when there is a persistent elevation in the force of blood against the walls of the arteries. Blood pressure is measured in millimeters of mercury (mm Hg), and hypertension is typically defined as a blood pressure reading of 130/80 mm Hg or higher.
Sandeep Bastikar • December 26, 2019
Write about something you know. If you don’t know much about a specific topic that will interest your readers, invite an expert to write about it.
Speak to your audience
Take a few moments to plan your post
Don’t forget to add images
Edit carefully before posting
Take a few moments to plan your post
Don’t forget to add images
Edit carefully before posting
You know your audience better than anyone else, so keep them in mind as you write your blog posts. Write about things they care about. If you have a company Facebook page, look here to find topics to write about
Once you have a great idea for a post, write the first draft. Some people like to start with the title and then work on the paragraphs. Other people like to start with subtitles and go from there. Choose the method that works for you.
Be sure to include a few high-quality images in your blog. Images break up the text and make it more readable. They can also convey emotions or ideas that are hard to put into words.
Once you’re happy with the text, put it aside for a day or two, and then re-read it. You’ll probably find a few things you want to add, and a couple more that you want to remove. Have a friend or colleague look it over to make sure there are no mistakes. When your post is error-free, set it up in your blog and publish.
Blood pressure is categorized into four general ranges: Normal blood pressure: 120/80 mm Hg. Elevated blood pressure: The upper number ranges from 120 to 129 mm Hg, with the lower number not exceeding 80 mm Hg. Phase 1 hypertension: The upper number ranges from 130 to 139 mm Hg, or the lower number is between 80 and 89 mm Hg. Phase 2 hypertension: The upper number is 140 mm Hg or higher, or the lower number is 90 mm Hg or more. A reading higher than 180/120 mm Hg is considered a hypertensive emergency. Untreated high blood pressure can lead to serious health problems such as heart attacks, strokes, and more. Regular blood pressure checks are crucial, starting at age 18 and repeated at least every two years. While most individuals with high blood pressure do not exhibit symptoms, some may experience headaches, shortness of breath, or nosebleeds. However, these symptoms are usually not specific and may only appear when hypertension reaches a severe stage. Blood pressure is influenced by the amount of blood the heart pumps and the resistance encountered by the blood as it flows through the arteries. Two main types of hypertension are: Primary hypertension: This type has no identifiable cause and tends to develop gradually over time. Factors like plaque buildup in the arteries (atherosclerosis) can contribute to its progression. Secondary hypertension: This form results from an underlying condition and manifests suddenly, leading to higher blood pressure than primary hypertension. Conditions and drugs that can trigger secondary hypertension include adrenal gland tumors, congenital heart defects, certain medications, illegal drugs, kidney disease, sleep apnea, and thyroid problems. Sometimes, a health check-up alone can cause a temporary rise in blood pressure, known as white coat hypertension. Prolonged high blood pressure can damage blood vessels and vital organs, resulting in complications such as heart attacks, strokes, aneurysms, heart failure, kidney problems, eye issues, metabolic syndrome, memory and cognitive i impairments, and even dementia. Taking steps to prevent and manage high blood pressure through a healthy lifestyle, regular exercise, and dietary changes can help mitigate the risk. In some cases, medication may be necessary to control hypertension effectively.
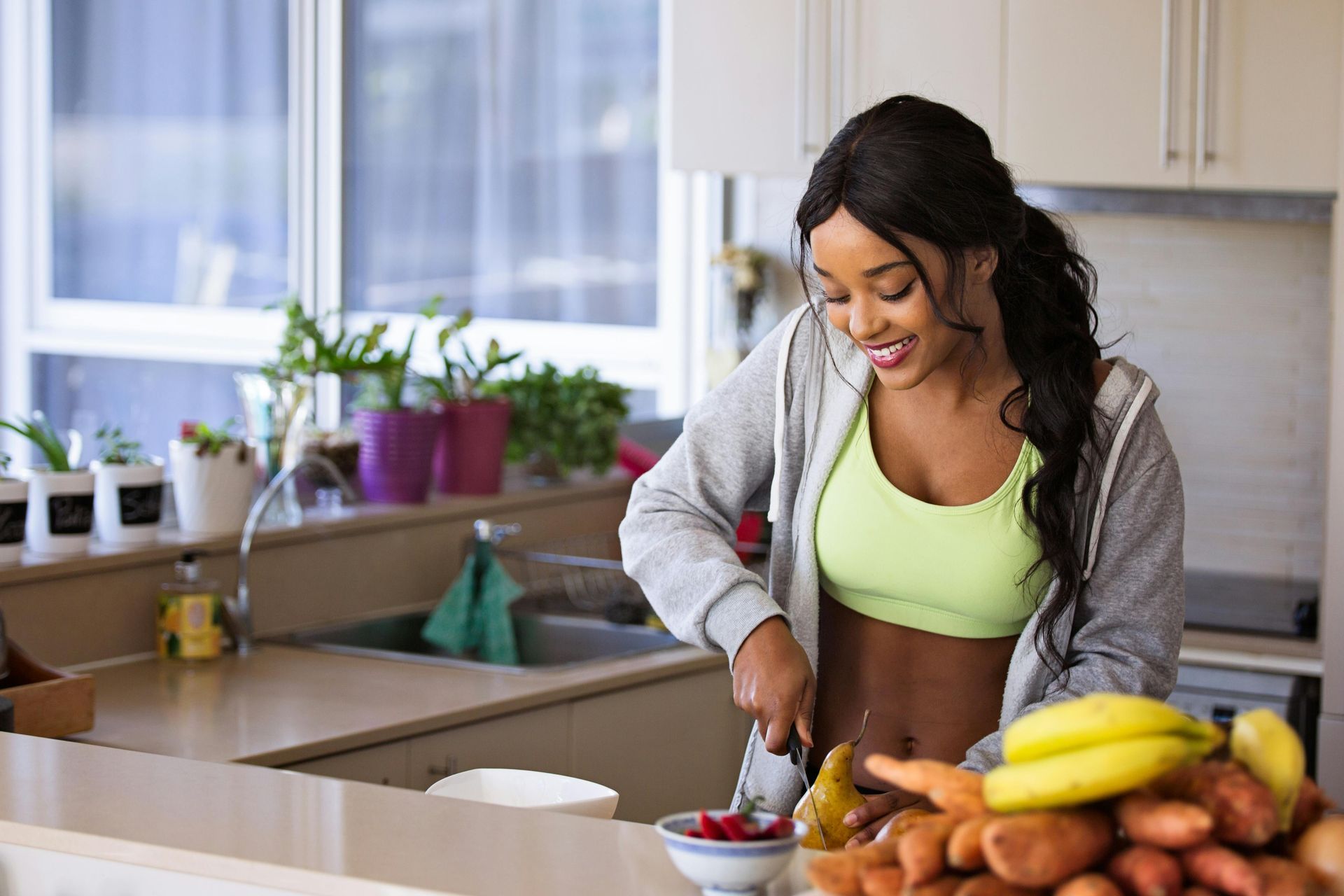

Enhancing Immunity: A Comprehensive Guide Optimize Your Gut Health Improving your immune system starts with enhancing your gut health. The gastrointestinal (GI) tract plays a pivotal role in our immune system. The intestinal lining produces antibodies and houses cells responsible for identifying and eliminating harmful bacteria. Balancing the good and bad bacteria in your gut is essential for optimal health. To promote good gut health, consider the following steps: Incorporate daily probiotics into your routine. Minimize the consumption of processed foods. If you have food sensitivities, contemplate removing items like gluten, dairy, and soy from your diet if they cause discomfort. Include Immunity-Boosting Foods Certain foods can significantly bolster your immune system: Mushrooms: A rich source of immune-boosting vitamin D, mushrooms can enhance white blood cell activity. Garlic: Allicin, a compound found in garlic, combats infection-causing microbes. Antioxidants: Consume a well-rounded diet consisting of unprocessed foods rich in antioxidants, such as leafy greens, mustard, and collard greens. Maintain Adequate Vitamin Levels Balanced vitamin levels are crucial for a robust immune system: Vitamin D: This vitamin is vital for immune health. Aim for daily doses of 2,000 IU to 5,000 IU. Vitamin C: Especially useful during periods of increased physical stress, vitamin C reduces the risk of common ailments like the cold. Daily intake should range from 1,000 mg to 5,000 mg, depending on your needs. Balance Hormones Maintaining balanced hormone levels, particularly estrogen and progesterone, is crucial to prevent autoimmune issues. Incorporate Herbs and Spices Include onions, garlic, ginger, black peppercorn, cayenne pepper, allspice, curry, and turmeric in your cooking. These ingredients contain components that can bolster your immune system. Stay Hydrated Proper hydration is one of the best ways to boost your immunity. Engage in Regular Exercise Cardiovascular exercises, such as running, jogging, and cycling, promote blood circulation and lymphatic fluid flow, r removing toxins and waste products. Aim for at least 30 to 40 minutes of cardio exercise five days a week. Manage Stress Mindfully Chronic stress can suppress the immune system. Manage stress through mindfulness techniques. Prioritize Adequate Sleep Getting seven to eight hours of sleep each night is crucial. Inadequate sleep can increase inflammation and weaken your ability to combat infections. Regularly Detoxify Regular detoxification is essential to alleviate the burden on your immune system. Incorporate detoxifying herbs like cilantro into your diet. Reduce Sugar Intake Limiting sugar consumption is vital, as it can cause inflammation, making your body more susceptible to illness. Limit Antibiotic Use Avoid antibiotics whenever possible, as they can disrupt beneficial gut bacteria and suppress immune functions. Explore natural alternatives first. Avoid Sharing Personal Items To minimize the risk of spreading germs, refrain from sharing personal items. Enjoy Life, Laugh, and Relax Chronic stress and depression can weaken the immune system, making us more susceptible to illness. Take time to savor life's pleasures. Start with Probiotics Incorporating probiotics into your diet can significantly enhance digestion and strengthen your immune system. Natural probiotic-rich foods like yogurt, kimchi, and miso are effective in promoting overall health. Prioritizing gut health is essential for a robust immune system.
